
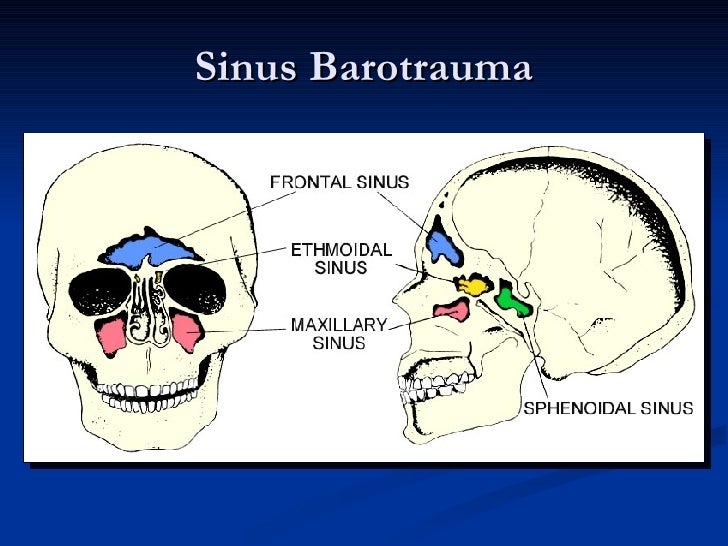
Larger lungs require larger breaths and consequently an increase in air consumption. The bigger the spill (in our comparison, this would be the amount of exercise which produces more carbon dioxide) and the bigger the carpet (in our example, the size of the person’s lungs), the more water you would need to rinse it clean - that is, the more air you will require to wash the carbon dioxide out. The truth of the matter is that removing carbon dioxide from the lungs is very analogous to rinsing dye out of a carpet. Many divers boast about low air consumption or try to artificially reduce their air consumption by skip breathing. Ear pain is mostly quite obvious, but it is always worth asking whether ear equalizing was easy and effective during a dive. Sinus pain is usually over the forehead or cheekbones or sometimes behind the eyes or on top of the head.

Pain related to neck problems is usually a persisting non-throbbing pain that gradually spreads from the back of the head to the temples. Where is the pain, and what does the pain feel like? The solution is to ensure that the neck, when extended normally, does not bring the head against the pillar valve by simply adjusting the position of the cylinder as needed. Is the diver constantly avoiding the pillar valve by bending the part of the neck closest to the shoulders downwards, and then having to hyperextend the part closest to the skull to curl around the valve? As odd as this may sound, it is a very common cause of headache in divers. What is the position of your tank on your back? Some report improvement after visiting a chiropractor. Physiotherapy and muscle strengthening exercises are often of value. A medical specialist such as an orthopedic surgeon should assess these problems. The underlying bony problems lead to muscle spasms, which in turn cause the headache. Divers with previous neck or upper back problems or injuries are very prone to develop headaches underwater or even as a result of a bumpy boat trip. In the end, it is always better to own your own equipment once you have found what works for you. Swapping regulators or trying different mouthpieces may spell the end of a continuous string of headaches. A bad-fitting mouthpiece can also cause headache: Some regulators are quite heavy in the water and require a constant “bite” to stay in place. Headaches may also result from tension, large caffeine intake and menstrual changes, among other reasons. Such headaches, especially if they are associated with symptoms of nausea, vomiting, abnormal sensations, vision, abnormal smell or even paralysis, may be serious and require assessment by a specialist neurologist.Migraine, a relative contraindication to scuba diving, requires expert assessment. Have you had previous head or neck problems, injuries or regular headaches, even when not diving?ĭivers who develop headaches regularly above water are also very likely to get them underwater. These five key questions may provide an answer to the causes of headaches:ġ.

However, important clues can usually be found in the history taken from someone who develops headaches regularly. The origins of headaches are truly diverse. While not an exhaustive list, possible sources may include: One way to find the cause of a headache is to run through a checklist of possible causes and eliminate them one by one. To help alleviate the pain and discomfort associated with constant headaches, it’s important to try and figure out a potential cause. But when headaches are a recurring issue for divers, that’s when it becomes concerning. Many divers have experienced a headache after a dive with it eventually clearing and no lasting side effects.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
